Harnessing Nature's Power: How Polyphenols and Phytonutrients Boost Athletic Performance
 Karen Parnell
August 19, 2023
Karen Parnell
August 19, 2023
Harnessing Nature's Power: How Polyphenols and Phytonutrients Boost Athletic Performance
.jpg)
Photo by Anna Pelzer on Unsplash
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Your journey as a triathlete to race day demands the fusion of stamina, rapid recovery, and an unyielding spirit. In your relentless pursuit to do your best, a natural ally awaits – the dynamic duo of polyphenols and phytonutrients.
In a recent review from the University of Padova they concluded polyphenols “promote athletic performance by improving cardiometabolic functions, reducing recovery times and post-exercise pain, maintaining a low degree of oxidative stress, and avoiding dysregulated inflammatory processes”.
With every stroke in the water, mile on the bike, and stride on the road, your body faces a variety of challenges and tests. That's where polyphenols and phytonutrients come into play, providing a helping hand with your unique journey. Found abundantly in foods like berries, leafy greens, and nuts, these compounds offer a toolkit to elevate your triathlon performance.
In this article we will discuss the advantages these compounds bring to triathletes like you. From increasing cardiovascular endurance and mitigating post-race inflammation to fuelling muscle recovery after each training sessions, polyphenols and phytonutrients stand ready to become your trusted partners in the pursuit of the podium.
We will cover the natural way to include polyphenols and phytonutrients in your diet and some example meal recipes and snacks.
Let's start by understanding what polyphenols and phytonutrients are, and then we can delve into their advantages for various athletic activities.
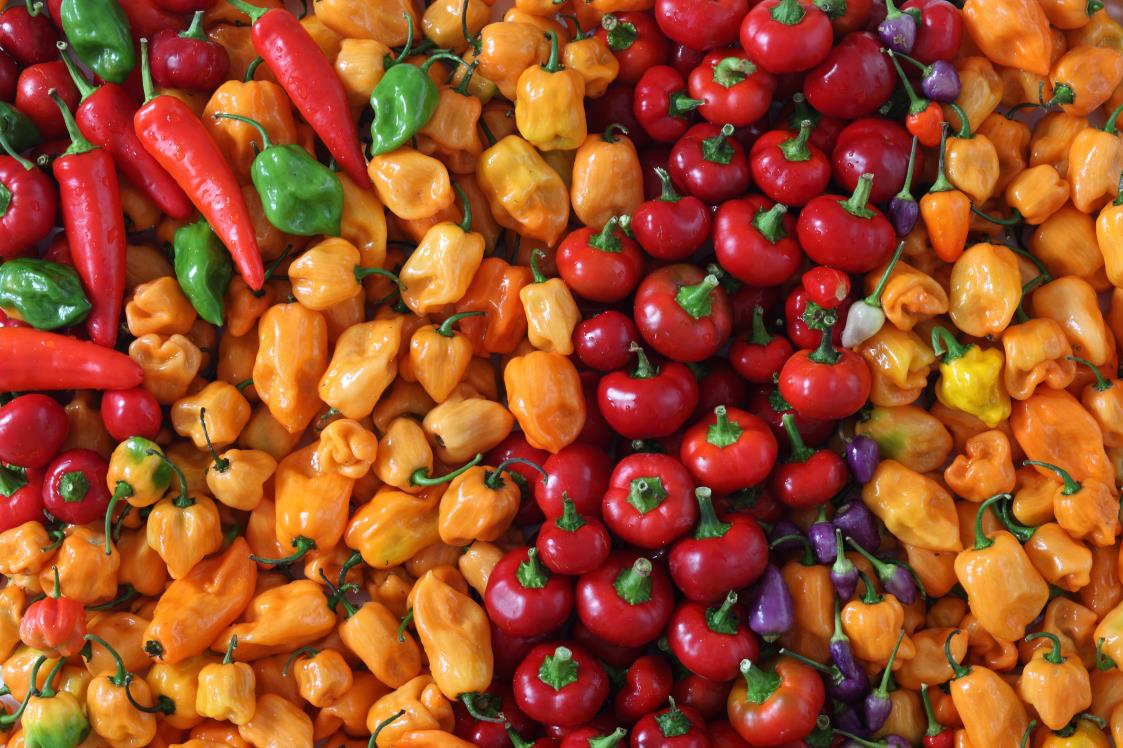

Colour is Key when it comes to locating Polyphenols and Phytonutrients. Photo by Randy Fath on Unsplash
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
What are Polyphenols and Phytonutrients?
Phytonutrients, also known as phytochemicals, are natural compounds found in plants. While not considered essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals, they have been shown to have various health-promoting effects when consumed in the diet.
Phytonutrients contribute to the vibrant colours, flavours, and aromas of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and other plant-based foods. These compounds play a crucial role in the plant's defence mechanisms against environmental stressors, such as UV radiation and pests. When humans consume these plant foods, they can potentially experience health benefits due to the diverse and often potent biological activities of phytonutrients. These benefits can range from antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects to supporting immune function and overall well-being.
Polyphenols are a group of naturally occurring compounds found in plants. They are a type of phytonutrient, known for their diverse health-promoting properties. Polyphenols encompass a wide range of subtypes, such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes, each with its own unique characteristics. These compounds are found in various plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, tea, coffee, and red wine.
One of the remarkable features of polyphenols is their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential, which supports the body's defence against oxidative stress and inflammation. Polyphenols have gained attention for their potential to enhance heart health, improve cognitive function, and even contribute to longevity. As part of a balanced diet rich in colourful plant foods, polyphenols can provide an array of health benefits, making them a valuable component of a nutritious lifestyle.
How They Help the Human Body
Both polyphenols and phytonutrients are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They support the body's defence against oxidative stress, which is a common occurrence during intense exercise and physical training. Oxidative stress can lead to muscle damage, inflammation, and decreased performance, which is why incorporating polyphenols and phytonutrients into the diet can be particularly beneficial for athletes.
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Benefits for Triathletes
1. Swimming
Improved blood flow - Polyphenols have been shown to enhance blood flow, which can be advantageous for swimmers by delivering more oxygen to muscles and improving overall endurance.
Anti-inflammatory effects - Phytonutrients can help reduce post-swimming inflammation and muscle soreness, aiding in quicker recovery between swim sessions.
2. Cycling
Enhanced endurance - Polyphenols, such as those found in berries and green tea, have the potential to improve endurance by increasing oxygen utilization and reducing fatigue.
Muscle recovery - The anti-inflammatory properties of phytonutrients can support muscle recovery after demanding cycling sessions.
3. Running
Joint health - Certain polyphenols, like those in cherries and turmeric, have anti-inflammatory effects that can help protect joints, reducing the risk of running-related injuries.
Energy production - Phytonutrients in foods like bananas and sweet potatoes can contribute to sustained energy levels during runs.
4. Strength Training
Muscle repair - Polyphenols assist in muscle repair and growth by promoting protein synthesis and reducing muscle damage resulting from intense strength training.
Anti-catabolic effects - Phytonutrients can help prevent muscle breakdown and support muscle retention during periods of high-intensity training.
5. Recovery
Reduced muscle soreness - Polyphenols and phytonutrients aid in reducing post-workout muscle soreness, enabling faster recovery, and preparing athletes for subsequent training sessions.
Cellular repair - These compounds support cellular repair and regeneration, contributing to overall recovery from strenuous activities.
.jpg)
Polyphenols and Phytonutrients are a triathletes best friend Photo by Victoire Joncheray on Unsplash
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Benefits of Polyphenols and Phytonutrients for All Athletes
There is a growing body of research that supports the idea that polyphenols and phytonutrients can be beneficial for athletes. While more studies are needed to fully understand the mechanisms and potential benefits, here are some key findings from existing research:
1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Exercise, especially intense training, can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Polyphenols, due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, have been shown to counteract these effects, reducing exercise-induced damage, and supporting recovery.
2. Enhanced Endurance
Certain polyphenols, such as those found in green tea (catechins) and berries (anthocyanins), have been linked to improved endurance. These compounds may enhance oxygen utilization, increase fat oxidation, and improve overall stamina, benefiting endurance athletes.
3. Muscle Recovery and Repair
Polyphenols and phytonutrients can aid in muscle recovery and repair by promoting protein synthesis and reducing muscle damage caused by intense exercise. This can be particularly valuable for athletes engaged in strength training and high-intensity workouts.
4. Immune System Support
The immune system can be temporarily compromised after intense exercise. Phytonutrients, including those found in colourful fruits and vegetables, play a role in maintaining immune function. This is important for athletes to avoid illness and maintain consistent training.
5. Reduced Muscle Soreness
The anti-inflammatory properties of certain polyphenols, such as those found in cherries and turmeric, may help reduce muscle soreness and discomfort after strenuous workouts, enhancing an athlete's ability to recover and train effectively.
6. Cardiovascular Health
Some polyphenols, like those in red grapes and dark chocolate, have been associated with improved cardiovascular health. This can benefit athletes by supporting efficient oxygen delivery and circulation during exercise.
7. Gut Health
Phytonutrients found in whole plant foods can contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut microbiome is linked to improved nutrient absorption, digestion, and overall well-being, which are important for athletes' performance.
8. Adaptogenic Effects
Certain polyphenols, known as adaptogens, have been suggested to help the body adapt to stress, potentially aiding athletes in managing the physical stress of intense training.
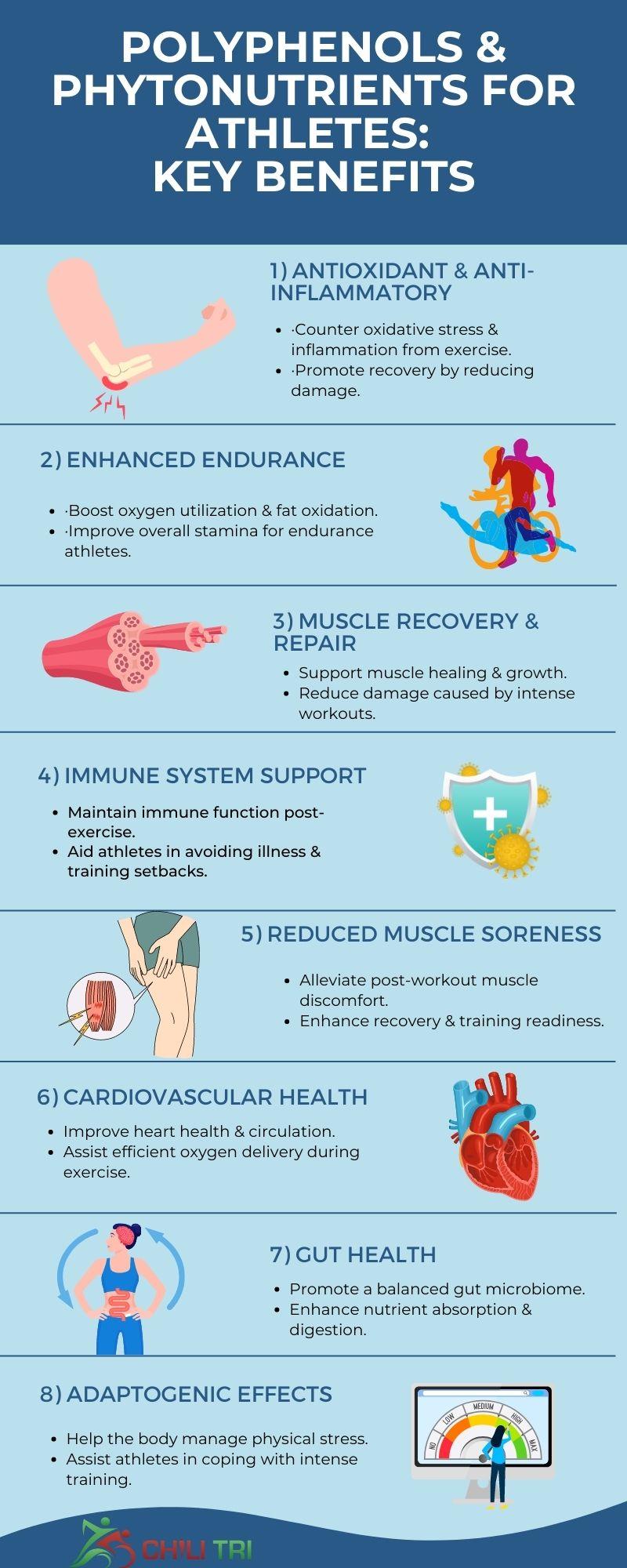
Summary of the benefits of Polyphenols and phytonutrients for athletes
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Examples of foods that are rich in Polyphenols and Phytonutrients
Polyphenol Rich Foods
Polyphenols are found in a wide range of plant-based foods, and incorporating a variety of these foods into an athlete's diet can provide numerous health benefits. Here are some examples:
Berries - Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries are packed with anthocyanins, a type of polyphenol known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Green Tea - Green tea is rich in catechins, which have been linked to improved endurance, increased fat oxidation, and enhanced cardiovascular health.
Dark Chocolate - Dark chocolate, especially varieties with high cocoa content, contains flavonoids that contribute to heart health and may improve blood flow.
Red Grapes - Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in red grapes, has been associated with various health benefits, including anti-aging properties and cardiovascular protection.
Nuts - Walnuts, almonds, and pecans contain polyphenols that support brain health and provide a source of healthy fats and protein.
Spices - Turmeric, cinnamon, and ginger are rich in polyphenols with potent anti-inflammatory effects, which can aid recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
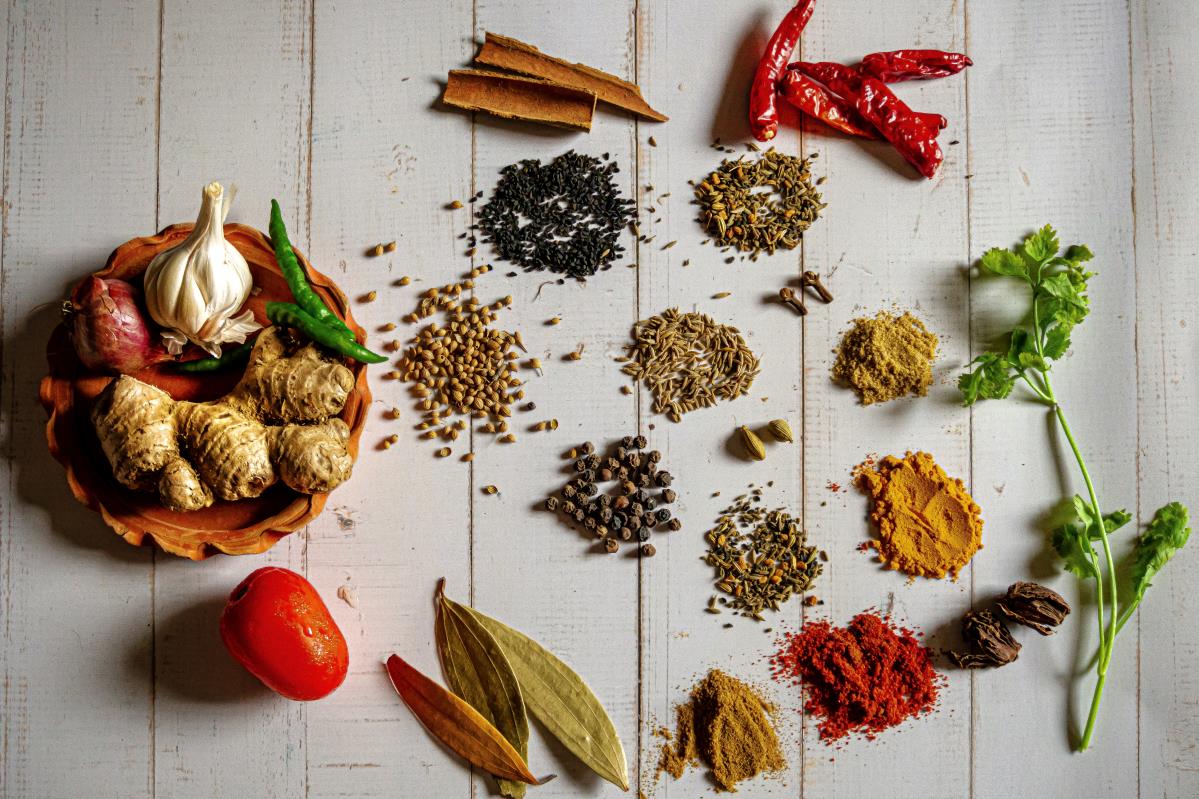

Add spices to your meals to help reduce inflammation, aid recovery and reduce muscle soreness
Photo by Ratul Ghosh on Unsplash
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Foods Rich in Phytonutrients
Phytonutrients encompass a wide range of compounds found in plant foods that offer health-promoting effects. Here are some examples of foods rich in phytonutrients:
Leafy Greens - Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are packed with phytonutrients like chlorophyll, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which support eye health and overall well-being.
Cruciferous Vegetables - Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol, phytonutrients that have been linked to cancer prevention and detoxification.
Citrus Fruits - Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are loaded with vitamin C and flavonoids, contributing to immune support and collagen synthesis.
Tomatoes - Tomatoes contain lycopene, a phytonutrient with antioxidant properties that may help protect against exercise-induced oxidative stress.
Legumes - Beans, lentils, and chickpeas provide a mix of phytonutrients such as flavonoids and lignans, supporting heart health and digestion.
Colourful Vegetables - Carrots, sweet potatoes, and bell peppers are high in beta-carotene, which converts to vitamin A and supports skin health and immune function.
Variety is key when it comes to obtaining a broad spectrum of polyphenols and phytonutrients. By including an array of colourful fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and herbs in your diet, you can maximize the intake of these beneficial compounds and reap their potential benefits for athletic performance and overall health.
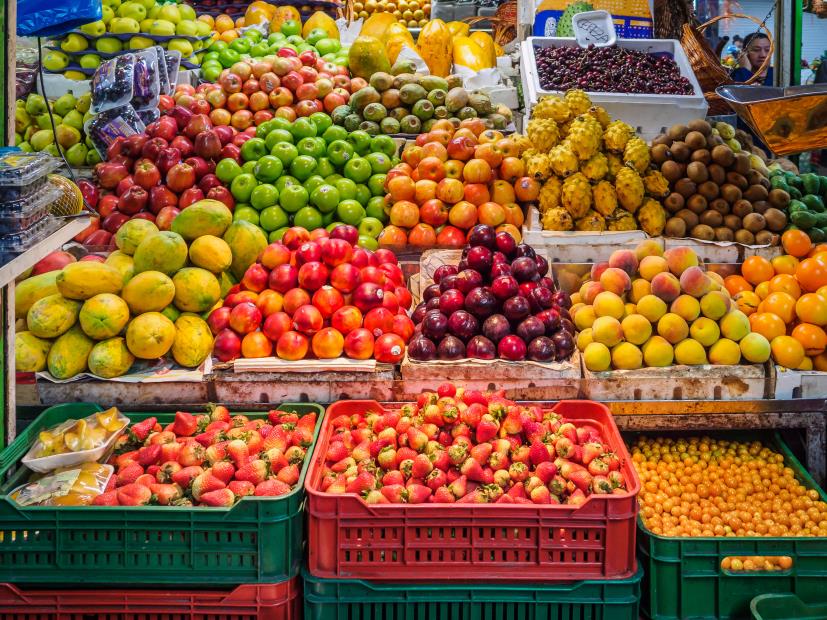

Include a colourful array of fruit and vegetables in your diet for optimal performance Photo by Alexander Schimmeck on Unsplash
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
A Day filled with Polyphenols and Phytonutrients
Here's a sample menu and recipes for a day that includes breakfast, lunch, and dinner, focusing on foods rich in polyphenols and phytonutrients.
Breakfast: Blueberry Oatmeal Bowl
.jpg)
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Ingredients
- 1/2 cup rolled oats
- 1 cup almond milk (or any milk of your choice)
- 1/2 cup fresh blueberries
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1 tablespoon chopped walnuts
- 1 teaspoon honey or maple syrup (optional)
Instructions
In a saucepan, combine oats and almond milk. Cook over medium heat until the oats are tender, and the mixture thickens.
Remove from heat and stir in chia seeds.
Transfer to a bowl and top with blueberries, chopped walnuts, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup.
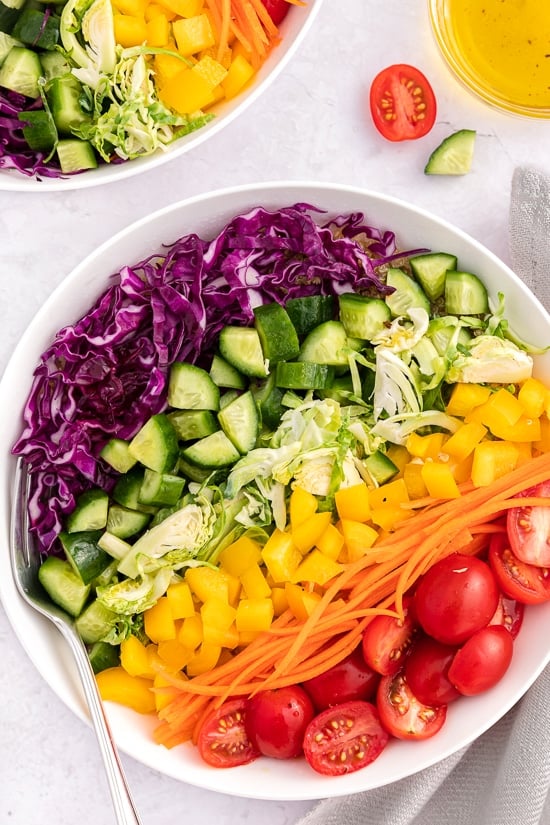
Lunch: Rainbow Quinoa Salad

Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Ingredients
1 cup cooked quinoa (cooled)
1 cup mixed leafy greens (spinach, kale, arugula)
1/2 cup cherry tomatoes, halved.
1/4 cup diced bell peppers (various colours)
1/4 cup shredded carrots
1/4 cup chopped cucumber
1/4 cup cooked chickpeas
2 tablespoons chopped fresh herbs (parsley, basil, mint)
Juice of 1 lemon
1 tablespoon extra-virgin olive oil
Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions
In a large bowl, combine cooked quinoa, mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, bell peppers, shredded carrots, cucumber, and chickpeas.
In a small bowl, whisk together lemon juice, olive oil, salt, and pepper to make the dressing.
Drizzle the dressing over the salad and toss to combine. Top with fresh herbs.
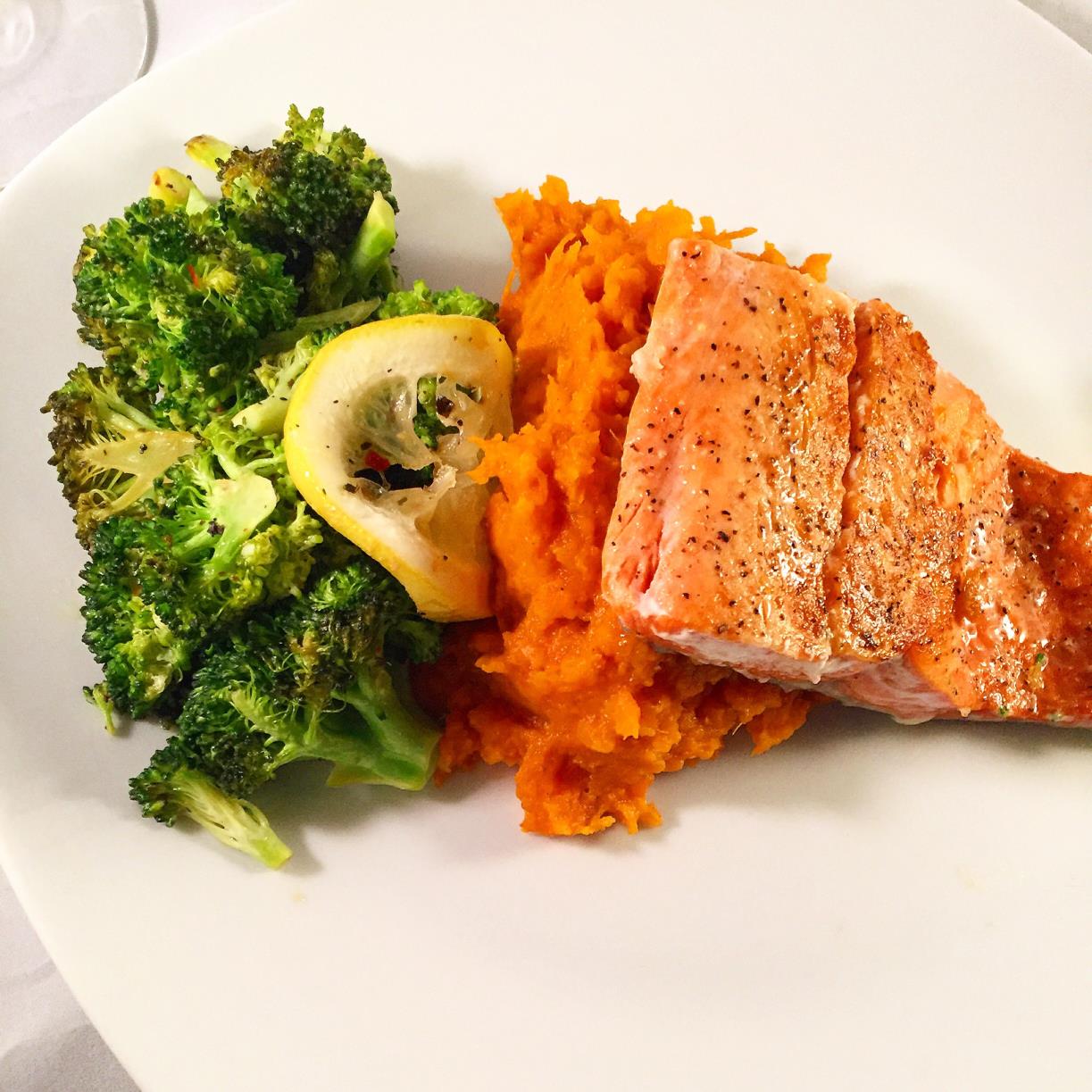
Dinner: Grilled Salmon with Steamed Broccoli and Roasted Sweet Potatoes

Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Ingredients
1 salmon fillet
1 teaspoon olive oil
Salt and pepper to taste
1 cup broccoli florets, steamed
1 medium sweet potato, diced
1 teaspoon coconut oil
1/2 teaspoon paprika
1/4 teaspoon cinnamon
Fresh lemon wedges for serving
Instructions
Preheat the grill. Brush the salmon fillet with olive oil and season with salt and pepper. Grill until cooked through.
In a skillet, melt coconut oil over medium heat. Add diced sweet potato and sprinkle with paprika and cinnamon. Cook until tender and slightly caramelized.
Steam broccoli until crisp-tender.
Serve the grilled salmon with steamed broccoli and roasted sweet potatoes. Squeeze fresh lemon juice over the salmon before enjoying.
This menu provides a balanced and colourful selection of foods rich in polyphenols and phytonutrients. You can customize these meals based on your dietary preferences and any specific nutritional needs you may have.
If you would like more recipe ideas you can download our FREE recipe books.
Polyphenol and Phytonutrient Rich Health Snacks
Here are some healthy snack ideas that are rich in polyphenols and phytonutrients if you want to augment your normal meals and fuel your training sessions.
1. Mixed Berry Parfait
Layer Greek yogurt with a variety of mixed berries (such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries). Top with a sprinkle of chopped nuts (like almonds or walnuts) for added crunch and healthy fats. Drizzle with a touch of honey or a sprinkle of cinnamon for extra flavour.
2. Veggie Sticks with Hummus
Slice colourful veggies like carrots, bell peppers, cucumber, and celery into sticks. Pair them with a serving of hummus for a satisfying and nutrient-rich snack.
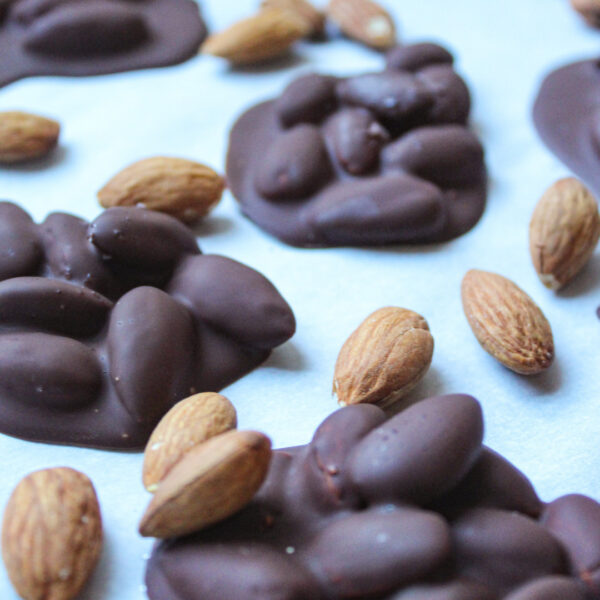
3. Dark Chocolate-Covered Almonds
Choose dark chocolate with a high cocoa content (70% or higher). Dip raw almonds in melted dark chocolate and allow them to cool and harden before enjoying.

Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
4. Fruit Salad
Create a colourful fruit salad using a mix of fruits like kiwi, oranges, grapes, and pomegranate seeds. Squeeze a little fresh lime or lemon juice over the fruit for a zesty twist.
5. Trail Mix
Make your own trail mix by combining a variety of nuts (such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews) with dried fruits (like cranberries, apricots, and raisins). Add a sprinkle of dark chocolate chips for a touch of sweetness.
6. Guacamole with Sliced Veggies
Prepare homemade guacamole using ripe avocados, chopped tomatoes, onions, cilantro, lime juice, and a pinch of salt. Serve with sliced veggies like bell peppers, cucumber, and jicama.
7. Greek Yogurt with Berries and Nuts
Mix plain Greek yogurt with fresh berries and a handful of mixed nuts for a protein-packed and satisfying snack.
8. Apple Slices with Nut Butter
Slice an apple and spread nut butter (such as almond or peanut butter) on the slices. Top with a sprinkle of chia seeds or cinnamon for added flavour and nutrients.
9. Roasted Chickpeas
Toss cooked chickpeas with a drizzle of olive oil and your favourite spices (such as paprika, cumin, and garlic powder). Roast in the oven until crispy and enjoy as a crunchy snack.
10. Green Smoothie
Blend together leafy greens (like spinach or kale), a variety of fruits (such as banana, mango, and pineapple), and a liquid base (such as almond milk or coconut water). Add a scoop of chia seeds or flaxseeds for an extra boost of nutrients.
These snack ideas offer a delicious way to incorporate polyphenols and phytonutrients into your daily routine while keeping your energy levels up and supporting your overall health and athletic performance.

If you would like some more healthy snack ideas download our FREE book.
Real Food Versus Supplementation
In a review by Aleksandra Duda-Chodak and Tomasz Tarko looking into the Possible Side Effects of Polyphenols and Their Interactions with Medicines have drawn the following conclusions:
“It should be clearly emphasized that, in general, polyphenols are safe for healthy individuals when consumed as a part of a balanced and varied diet. They are valuable natural compounds which help to prevent and treat many diseases or defend against various kinds of stress. Therefore, polyphenols should be introduced into our diet, especially as components of natural, low- or non-processed food such as fruit, vegetables, nuts, herbs, spices, tea, or juices”.
“However, the risk of possible negative side effects increases when polyphenols are consumed in large amounts without medical supervision in the form of dietary supplements or as various plant extracts. Such products usually contain huge doses of polyphenols which are often in the form of chemically purified aglycones (instead of glycosides which are present in “natural” food) that are impossible to achieve by normal food consumption”.
“The negative effects of polyphenols are also more likely to occur when a polyphenol-rich diet or supplements are taken by people being treated for various chronic illnesses who are required to take prescribed medications each day. Therefore, the authors of the review claim that it is very important to raise public awareness about the possible side effects of flavonoid supplementation, especially in the case of various vulnerable subpopulations”.
As an athlete it’s always best to eat “food first” rather than leaning on supplements.
Conclusion: Polyphenols and phytonutrients for Athletes
Polyphenols and phytonutrients offer a range of benefits for athletes, particularly triathletes engaged in swimming, cycling, running, strength training, and recovery. Their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and tissue repair properties can help enhance endurance, reduce muscle damage, alleviate soreness, and support overall performance.
Incorporating a variety of colourful fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and herbal teas into the diet can provide a diverse array of these beneficial compounds.
It’s best to get polyphenols and phytonutrients from real food in your diet rather than via supplementation.
However, it's important to note that individual responses to polyphenols and phytonutrients can vary, so athletes should experiment to find the foods and quantities that work best for them. Always consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist before making significant dietary changes.
Karen Parnell is a Level 3 British Triathlon Coach, 8020 Endurance and IRONMAN Certified Coach, WOWSA Level 3 open water swimming coach and NASM Personal Trainer and Sports Technology Writer. Karen has a certificate in Sport Nutrition and Advanced Clinical Weightless Practitioner.
Need a training plan? I have plans on TrainingPeaks and FinalSurge marketplace:
I also coach a very small number of athletes one to one for all triathlon distances, open water swimming events and running races, email me for details and availability. karen.parnell@chilitri.com
Get your FREE Athlete Recipe Books
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Polyphenols and Phytonutrients
What are Phytonutrients?
Phytonutrients, also known as phytochemicals, are natural compounds found in plants. While not considered essential nutrients like vitamins and minerals, they have been shown to have various health-promoting effects when consumed in the diet. Phytonutrients contribute to the vibrant colours, flavours, and aromas of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and other plant-based foods.
These compounds play a crucial role in the plant's defence mechanisms against environmental stressors, such as UV radiation and pests. When humans consume these plant foods, they can potentially experience health benefits due to the diverse and often potent biological activities of phytonutrients. These benefits can range from antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects to supporting immune function and overall well-being.
What are polyphenols?
Polyphenols are a group of naturally occurring compounds found in plants. They are a type of phytonutrient, known for their diverse health-promoting properties. Polyphenols encompass a wide range of subtypes, such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes, each with its own unique characteristics.
These compounds are found in various plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, tea, coffee, and red wine. One of the remarkable features of polyphenols is their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential, which supports the body's defence against oxidative stress and inflammation. Polyphenols have gained attention for their potential to enhance heart health, improve cognitive function, and even contribute to longevity. As part of a balanced diet rich in colourful plant foods, polyphenols can provide an array of health benefits, making them a valuable component of a nutritious lifestyle.
What are the health benefits of polyphenols and phytonutrients?
Polyphenols and phytonutrients have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting the body's defence against oxidative stress and inflammation. They are associated with improved cardiovascular health, enhanced immune function, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and better overall well-being.
What foods are rich in polyphenols?
Foods rich in polyphenols include berries (blueberries, strawberries, etc.), green tea, dark chocolate, red grapes, nuts (walnuts, almonds), and spices (turmeric, cinnamon). Consuming a variety of colourful fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based foods can provide a diverse range of polyphenols.
Which foods contain phytonutrients?
Phytonutrients are found in a wide array of plant foods. Examples include leafy greens (spinach, kale), cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower), citrus fruits (oranges, lemons), tomatoes, legumes (beans, lentils), and colourful vegetables (carrots, sweet potatoes).
Can polyphenols and phytonutrients improve athletic performance?
Yes, polyphenols and phytonutrients can potentially enhance athletic performance. Their anti-inflammatory effects may help reduce exercise-induced muscle damage and soreness, while their antioxidant properties can combat oxidative stress during intense training.
How can polyphenols and phytonutrients benefit endurance athletes?
Endurance athletes can benefit from improved oxygen utilization and reduced fatigue due to the presence of specific polyphenols. For example, green tea catechins and berries' anthocyanins have been linked to increased endurance.
Are there specific benefits for strength training athletes?
Polyphenols can aid muscle repair and growth by promoting protein synthesis, while certain phytonutrients may prevent muscle breakdown during intense strength training. Additionally, their anti-inflammatory effects can assist recovery.
Can these compounds aid in recovery after workouts?
Yes, polyphenols and phytonutrients support recovery by reducing muscle soreness, promoting cellular repair, and decreasing inflammation, allowing athletes to bounce back more quickly after strenuous workouts.
Should athletes consider supplements for polyphenols and phytonutrients?
While obtaining these compounds from whole foods is recommended, some athletes may consider supplements. However, it's best to consult a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as individual needs can vary.
Can polyphenols and phytonutrients help reduce exercise-induced inflammation?
Yes, the anti-inflammatory properties of these compounds can help mitigate exercise-induced inflammation, supporting the body's recovery process and overall immune function.
Are there any potential drawbacks or side effects of consuming polyphenols and phytonutrients?
In general, consuming a variety of plant-based foods rich in polyphenols and phytonutrients is safe and beneficial. However, excessive consumption of some supplements or foods might lead to unwanted effects. Moderation is key.
Can these compounds be integrated into a balanced diet for non-athletes as well?
Absolutely. Polyphenols and phytonutrients offer health benefits to individuals of all activity levels. A diet rich in these compounds supports overall well-being, regardless of athletic pursuits.
Individual responses to polyphenols and phytonutrients can vary, and it's important to consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist when making significant dietary changes or considering supplements. Incorporating a variety of colourful and nutrient-dense foods into your diet is the best way to enjoy the benefits of these compounds.
References
Polyphenols and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (fisiologiadelejercicio.com)
Possible Side Effects of Polyphenols and Their Interactions with Medicines - PMC (nih.gov)
Clinical Evidence of the Benefits of Phytonutrients in Human Healthcare - PMC (nih.gov)
Polyphenols: Potential Beneficial Effects of These Phytochemicals in Athletes - PubMed (nih.gov)
FSAS-JUNE-2021-Article-v1.pdf (fsacademy.co.za)
Phytonutrients as therapeutic agents - PubMed (nih.gov)

